Volatility Effects
Reward goes with risk, and volatility represents risk. Therefore, volatility means reward; investors/traders get paid for riding roller coasters. Right? These blog entries relate to volatility effects.
February 23, 2023 - Strategic Allocation, Volatility Effects
Is portfolio downside risk better manageable by combining drawdown and recovery into a single “submergence” metric? In their February 2023 paper entitled “Submergence = Drawdown Plus Recovery”, Dane Rook, Dan Golosovker and Ashby Monk present submergence density as a new risk metric to help investors analyze asset/portfolio drawdown and recovery jointly. They define submergence (s) of an asset/portfolio as percentage of current value below its past highwater mark. They define submergence density (d) during a given sample period as the κ-root of the sum of measurement interval submergences each raised to the κ-power during the sample period, as follows:
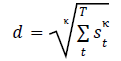
When κ=1, submergence density is arithmetic average drawdown. When κ=∞ (or a very high number), submergence density is maximum drawdown. They use κ = 5 in examples to represent typical investor drawdown sensitivity. They define submergence risk-adjusted return as excess return (relative to the risk-free rate) minus a fraction (Θ) of submergence density, using the range 0.2 to 0.5 as reasonable for Θ. They apply submergence to several market indexes and discuss portfolio diversification and rebalancing in the context of reducing submergence overlaps. Using monthly excess returns for U.S. stocks, corporate bonds and Treasuries (S&P 500 Index, ICE BoA Corporate Bond Index and Bloomberg Treasuries Index, respectively) during 1979 through 2022, they find that:
Keep Reading
February 15, 2023 - Technical Trading, Volatility Effects
Are there different patterns of short-term stock return reversal based on stock liquidity (measured by size, volatility or turnover)? In their January 2023 paper entitled “Reversals and the Returns to Liquidity Provision”, Wei Dai, Mamdouh Medhat, Robert Novy-Marx and Savina Rizova examine interactions between short-term reversal returns and stock liquidity metrics. They select reversal candidates from the fifth (quintile) of stocks with the highest (winners) and lowest (losers) industry-relative returns over the last 1, 5 or 21 trading days, excluding 3-day returns around earnings announcements. They separately sort stocks into quintiles by size (market capitalization), volatility (standard deviation of daily returns over the last 63 days) or turnover (average percentage of shares outstanding traded daily over the last 63 days). While the sample includes all NYSE, AMEX and NASDAQ common stocks, quintile breakpoints come from NYSE stocks only. Finally, they look at returns to value-weighted intersections of reversal candidate quintiles and size, volatility or turnover quintiles. Using the specified inputs for all listed U.S. common stocks, measured monthly, during January 1973 through December 2021, they find that:
Keep Reading
January 6, 2023 - Big Ideas, Volatility Effects
How should investors think about, and perhaps exploit, asset return volatility? In his December 2022 paper entitled “A Stylized History of Volatility”, Emanuel Derman reviews how generations of financial modelers have quantified volatility and ultimately created tradable volatility-based assets. He also discusses some general modeling considerations. Based on the body of research and his experience, he concludes that: Keep Reading
January 3, 2023 - Fundamental Valuation, Momentum Investing, Size Effect, Value Premium, Volatility Effects
Do the widely used U.S. stock return factors exhibit long-term trend changes and shorter-term cyclic behaviors? In his November 2022 paper entitled “Trends and Cycles of Style Factors in the 20th and 21st Centuries”, Andrew Ang applies various methods to compare trends and cycles for equity value, size, quality, momentum and low volatility factors, with focus on a breakpoint at the end of 2000. He measures size using market capitalization, value using book-to-market ratio, quality using operating profitability, momentum using return from 12 months ago to one month ago and low volatility using idiosyncratic volatility relative to the Fama-French 3-factor (market, size, book-to-market) model of stock returns. He each month for each factor sorts stocks into tenths, or deciles, and computes gross monthly factor return from a portfolio that is long (short) the average return of the two deciles with the highest (lowest) expected returns. As a benchmark, he uses the value-weighted market return in excess of the U.S. Treasury bill yield. Using market and factor return data from the Kenneth French data library during July 1963 through August 2022, he finds that:
Keep Reading
December 22, 2022 - Equity Premium, Strategic Allocation, Volatility Effects
A subscriber requested evaluation of a strategy that seeks to exploit U.S stock market reversion after dips by temporarily applying margin. Specifically, the strategy:
- At all times holds the U.S. stock market.
- When the stock market closes down more than 7% from its high over the past year, augments stock market holdings by applying 50% margin.
- Closes each margin position after two months.
To investigate, we assume:
- The S&P 500 Index represents the U.S. stock market for calculating drawdown over the past year (252 trading days).
- SPDR S&P 500 (SPY) represents the market from a portfolio perspective.
- We start a margin augmentation at the same daily close as the drawdown signal by slightly anticipating the drawdown at the close.
- 50% margin is set at the opening of each augmentation and there is no rebalancing to maintain 50% margin during the two months (42 trading days) it is open.
- If S&P 500 Index drawdown over the past year is still greater than 7% after ending a margin augmentation, we start a new margin augmentation at the next close.
- Baseline margin interest is U.S. Treasury bill (T-bill) yield plus 1%, debited daily.
- Baseline one-way trading frictions for starting and ending margin augmentations are 0.1% of margin account value.
- There are no tax implications of trading.
We use buying and holding SPY without margin augmentation as a benchmark. Using daily levels of the S&P 500 Index, daily dividend-adjusted SPY prices and daily T-bill yields from the end of January 1993 (limited by SPY) through November 2022, we find that: Keep Reading
October 10, 2022 - Equity Premium, Volatility Effects
Market commentators sometimes cite a high Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) Volatility Index (VIX), the options-implied volatility of the S&P 500 Index as an indicator of investor sentiment and therefore a contrarian signal for the stock market. Specifically, a relatively high (low) VIX indicates panic (complacency) and therefore pending stock market strength (weakness). Does evidence support such conventional wisdom? To check, we relate the level of VIX to S&P 500 Index returns over the next 5, 10, 21, 63 and 126 trading days. Using daily closes for VIX and the S&P 500 Index during January 1990 (limited by the VIX series) through September 2022, we find that: Keep Reading
September 23, 2022 - Strategic Allocation, Volatility Effects
The body of research indicates that low-volatility/low-beta stock investing suppresses exposure to overall equity market risk. Does it work equally well for different sources of such risk? In his September 2022 paper entitled “Macro Risk of Low-Volatility Portfolios”, David Blitz examines the separate exposures of low-volatility portfolios to interest rate, implied volatility, liquidity, commodity, sentiment, macroeconomic and climate (CO2 emissions) risk factors. Specifically, he compares the contemporaneous interactions with these risks of the MSCI USA Minimum Volatility Index (based on minimum variance optimization), the S&P 500 Low Volatility Index (the 100 inverse volatility-weighted stocks in the S&P 500 with the lowest volatilities over the past one year) and the S&P 500 Index as the market benchmark. He measures risk factor-index interactions via univariate regressions of monthly excess returns versus monthly risk factor values. He also considers risk factor interactions with ten (decile) equally weighted portfolios of the 1,000 largest U.S. stocks at each point in time sorted by preceding 36-month volatilities. Using monthly total returns for the indexes/portfolios in U.S. dollars in excess of the risk-free rate and monthly risk factor values during January 1991 through December 2021, he finds that:
Keep Reading
August 24, 2022 - Volatility Effects
A subscriber asked about frequency, magnitude and duration of bear market rallies. To investigate, we employ the S&P 500 Index and consider three ways to define a bear market:
- From the day the index is first down over 20% from a prior peak until the day it closes no more than 20% down (< -20% Drawdown).
- From the day the index is first down over 30% from a prior peak until the day it closes nor more than 30% down (< -30% Drawdown).
- From the day the index crosses below its 200-day simple moving average until the day it crosses back above this moving average (SMA200).
Based on bear market statistics for these three definitions, we then look at ways to characterize bear market rallies. Using daily S&P 500 Index closes from the end of December 1927 through mid-August 2022, we find that: Keep Reading
August 4, 2022 - Investing Expertise, Mutual/Hedge Funds, Volatility Effects
Is past rolling maximum drawdown, a simple measure of recent downside risk, a useful indicator of future mutual fund performance? In their June 2022 paper entitled “Maximum Drawdown as Predictor of Mutual Fund Performance and Flows”, Timothy Riley and Qing Yan investigate whether style-adjusted maximum drawdown based on daily returns over the last 12 months usefully predicts mutual fund performance. To adjust for fund style differences, they subtract from each individual unadjusted drawdown the average unadjusted drawdown across all funds in the same style during the measurement interval. Their principal performance metric is alpha based on a 4-factor (market, size, book-to-market, momentum) model of stock returns. Using daily net returns for 2,188 actively managed long-only U.S. equity mutual funds that are at least two years old and have at least $20 million in assets during January 1999 through December 2019, they find that: Keep Reading
July 11, 2022 - Equity Premium, Momentum Investing, Size Effect, Value Premium, Volatility Effects
Multifactor funds offer rules-based, diversified exposures to firm/stock factors found to beat the market in academic studies. Do the funds beat the market in real life? In his June 2022 paper entitled “Multifactor Funds: An Early (Bearish) Assessment”, Javier Estrada assesses performance of such funds across U.S., global and emerging markets relative to that of corresponding broad capitalization-weighted indexes and associated exchange-traded funds (ETF). He focuses on multifactor funds with exposure to at least three factors that are explicitly marketed as multifactor funds. Using monthly total returns for 56 U.S.-based equity multifactor funds with at least three years of data and $10 million in assets from respective inceptions (earliest June 2014) through March 2022, and total returns for matched broad market indexes and ETFs, he finds that:
Keep Reading