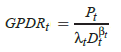Exploiting P/E10 to Time the U.S. Stock Market
December 27, 2016 - Fundamental Valuation
Is the relationship between Cyclically Adjusted Price to Earnings Ratio (CAPE, or P/E10) and future long-term stock market returns evidence of market inefficiency? In other words, can investors exploit P/E10 to beat the market? In their November 2016 paper entitled “Shiller’s CAPE: Market Timing and Risk”, Valentin Dimitrov and Prem Jain examine whether investors with a 10-year investment horizon can beat the market by holding either the S&P 500 Index or 10-year U.S. Treasury notes (T-notes) as a low-risk alternative according to whether P/E10 is low or high. Their methodology is comparison of averages and volatilities (standard deviations) of future 10-year nominal total returns by ranked tenth (decile) of monthly P/E10. They assume reinvestment of dividends and interest at a monthly frequency. Using monthly values of P/E10, stock market total returns (including dividends) and T-note yields from Robert Shiller’s database during January 1871 through August 2016, they find that: Keep Reading